New Delhi: At 58.8 percent, women’s participation in the Centre’s flagship Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee scheme (MGNREGS) in 2023-24 is the highest in the past decade, with several states such as Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Odisha, Punjab, Meghalaya reporting a significant increase, shows latest data available on rural development ministry’s portal.
The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act of 2005, which came into force in February 2006, guarantees 100 days of work or ‘person days’ to every registered rural household. The Act mandates that women make up at least a third of the scheme’s beneficiaries.
Over the years, there has been a gradual increase in the number of women seeking work under the scheme, the ministry data shows. Since 2013, there has been a 6.06 percentage point increase — 58.88 percent in 2023-24 from 52.82 percent in 2013-14 — in women’s participation in the rural job scheme.
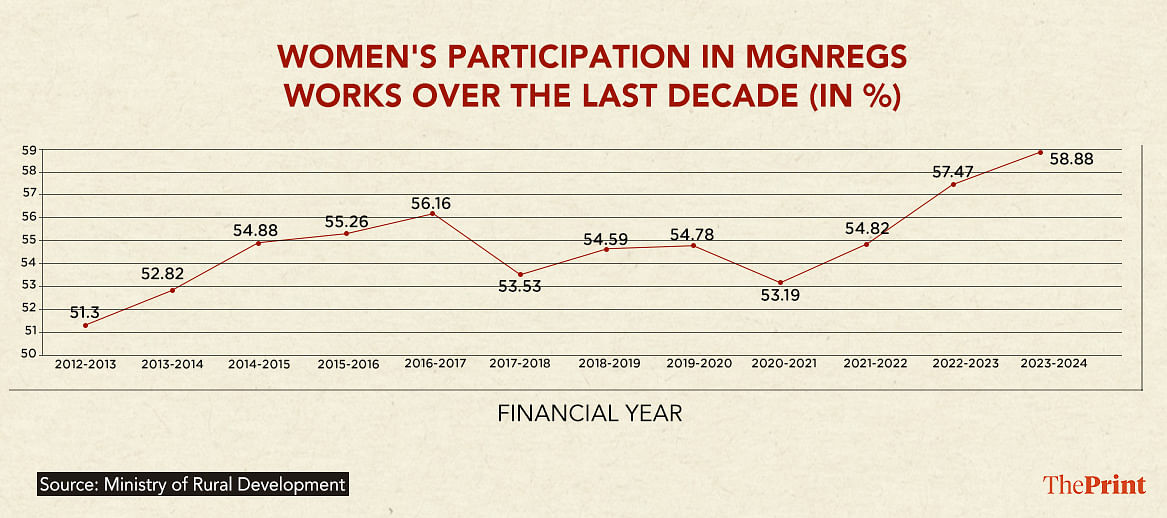
There was a sharp increase in the demand for work under MGNREGS during the pandemic years — 389 crore person days in 2020-21 and 363 crore in 2021-22 compared to 265 crore in 2019-2020 — due to reverse migration. The percentage of women availing the scheme was around 53-54 percent during the pandemic period.
In this financial year, 310 crore person days (including the additional person days offered by some states) have been generated as of 3 April, of which 182.97 crore person days (58.8 percent) — were of women, shows ministry data. In 2022-23, 57.47 percent of the workers who availed the scheme were women.
This gradual increase in women’s participation under MGNREGS is due to a host of reasons ranging from some states giving incentives for women workers, appointment of ‘women mates’ (who supervise work at MGNREGS sites and mark attendance of workers), involvement of women self help groups (SHGs) in rural jobs, etc.
State government officials in Uttar Pradesh and Gujarat said women SHGs, horticulture related jobs have played a role. “There are multiple reasons for the increase in women’s participation. The involvement of women SHG groups in MGNREGS works is an important contributing factor,” said a senior official with the UP government’s rural development department.
Prem Shankar, who works with Professional Assistance for Development Action (PRADAN) – a voluntary organisation that works in remote villages providing skill training to people from marginalised communities — in Jharkhand, said, “In the past few years, the Centre has been pushing states to employ women as mates. This along with the mandatory involvement of women in various development schemes such as preparation of village development plan has played an important role in increased women’s participation in schemes such as MGNREGS.”
He added, “Today, there is a lot of awareness among rural women about various state and central government schemes. The linking of MGNREGS works with the National Rural Livelihood Mission has also been a key factor in the increase in the number of women demanding work. Many states have announced state-specific innovative schemes for creating assets. A lot of women are involved in such work.”
Also Read: Centre increases MGNREGA wages by 3-10%. Haryana highest at Rs 374 per day, Arunachal lowest
How states fared in terms of women’s participation
BJP-ruled Uttar Pradesh has been among the states with the lowest women’s participation (between 24 and 34 percent) since the start of the scheme. But post-pandemic, UP, which has the highest number of households registered under MGNREGS, has witnessed a significant increase in the number of women demanding work — 42.27 percent in 2023-24 from 33.57 percent in 2020-21 (pandemic year).
According to ministry data, the proportion of women workers in Uttar Pradesh increased by 4.4 percentage points in 2023-24 — 42.27 percent compared to 37.87 percent in the preceding financial year of 2022-23.
UP-based activist Richa Singh, who works with MGNREGS workers in the state, said: “It was difficult for women in rural areas to work in public places or projects earlier due to opposition from families and village elders. But now, especially post-pandemic, women are coming out in large numbers due to various reasons. Men in rural areas migrating to other cities for better work opportunities is one of the reasons for increased women’s participation in the scheme.”
Like UP, Meghalaya, Gujarat and Assam have registered substantial increases in the number of women availing the scheme for work. In the Northeast, Meghalaya saw a 5.78 percentage point increase in the number of women person days in 2023-24 (57.3 percent) compared to 2022-23 (51.52 percent), while BJP-ruled states such as Gujarat and Assam saw a 3.51 percentage point and 3.06 percentage point increase respectively.
In Odisha, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Rajasthan, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Haryana and Assam — where there is high demand for work under MGNREGS — the increase in women’s participation from 2022-23 to 2023-24 ranged between 0.05 to over 2 percentage points, according to the ministry data.
States where women’s participation is over 60%
Kerala has traditionally topped the list of states where women’s participation in MGNREGS works is over 60 percent, at 89-90 percent over the last 10 years. In 2023-24, there was a marginal decrease in the rate of women’s participation — 89.27 percent in 2023-24 from 89.82 percent in 2022-23 — according to ministry data till 3 April.
Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan, Puducherry, Goa are among the other states and Union territories with 65-85 percent women’s participation in MGNREGS.
In 2023-24, Tamil Nadu had 86.66 percent women’s participation. In Goa, there was a 6 percentage point drop in women’s participation in 2023-24 — 72.41 percent in 2023-24 from 78.41 percent in 2022-23.
In 2023-24, these states and UT saw a marginal increase or decline in the percentage of women workers, but they continue to have a large number of women working under the rural employment scheme.
(Edited by Gitanjali Das)
Also Read: New geotag attendance feature becomes hassle for MGNREGS workers, states flag concerns to Centre



