Bengaluru: A grainy, breezy whoosh is what dust devils on Mars sound like when they pass right over a microphone. You can hear it in a recording — a historic first — made by NASA’s Perseverance rover as it encountered one of these storms in September last year.
The findings from one of the newest sets of data released by Perseverance were published in the journal Nature Communications this week.
Dust devils on Mars are very common, and appear like a mini-tornado on the surface, kicking up and transporting swirling dust on land. They primarily occur during the day and are driven by convection in the wispy layers of atmosphere from the distant sun. These convective vortices are especially common in the area of the Jezero Crater, the landing site of the Perseverance rover last year.
These whirlwinds play a key role in the mixing and dispersion of heat, dust, and surface minerals on the planet, and are indicators of atmospheric turbulence.
Understanding dust devils and how they work is an important part of understanding the Martian system for future space exploration and human trips to the red planet. In the process, planetary scientists also simulate these weather phenomena and predict dust storms on Mars. They’re also key to understanding how hardware on robots on Mars will last and function.
Among the newest sets of data released from Perseverance is the sound from a serendipitous and unexpected encounter with a dust devil. The rover carries microphones and cameras to record sights and sounds on Mars.
The data have enabled scientists to understand the physical properties of the storm and the conditions that led to its formation. Microphones also captured the sounds of sandy grains hitting the rover, providing information about the density of particles in the dust devil.
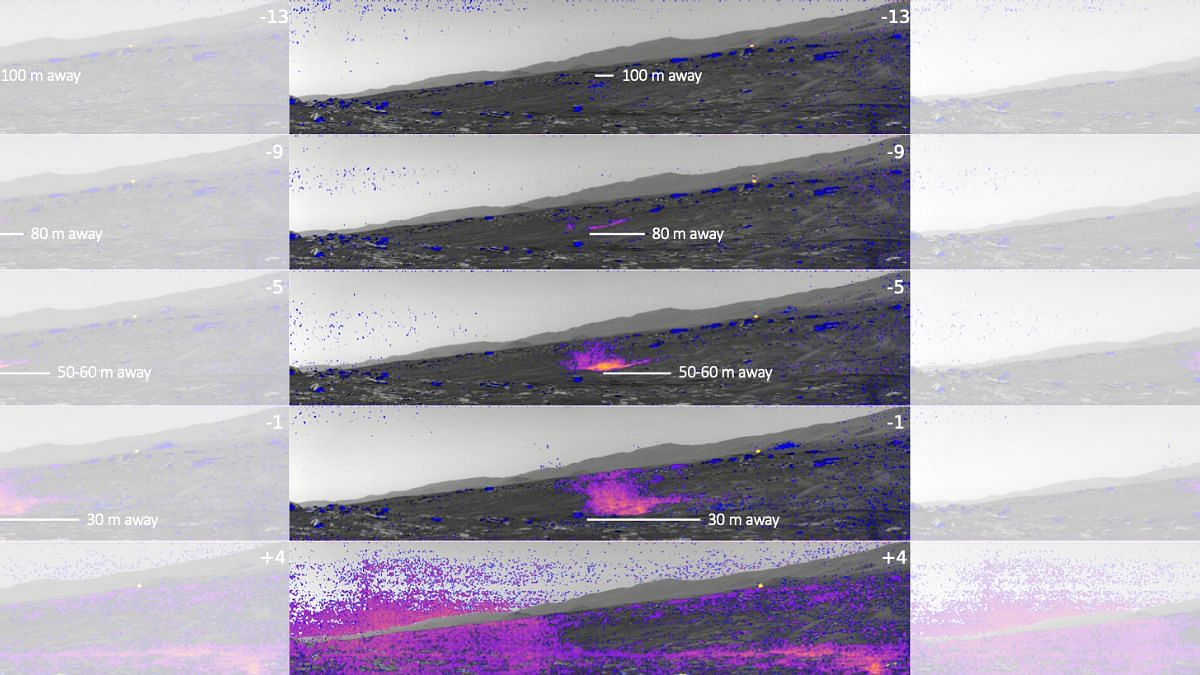
Naomi Murdoch from the University of Toulouse, France, and her colleagues, unexpectedly recorded the sound of a travelling Martian dust devil as it passed directly over the Perseverance rover on 27 September, 2021. The rover’s SuperCam microphone had recorded the sounds of the dust devil.
As the dust devil passed, the rover’s Navigation Camera (Navcam) and the Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA) instruments also made recordings of their own data.
Also read: ISRO-IISc team develops prototype of bacteria-infused bricks for Martian, lunar soil
‘9/10 the height of the pyramid of Giza’
The MEDA instrument has seven radiation and dust sensors and eight detectors that record changes in atmospheric pressure and aid in the detection of dust devils. In the first 216 sols (Martian days), 91 dust devils were detected. During the 167 seconds that the September dust devil passed over the rover, the instruments detected a drop in atmospheric pressure.
Combined with data from previous dust devils since the mission began and the way these mini storms moved, the team concluded that the September encounter was a hugely advantageous coincidence.
The SuperCam microphone acoustic recording shows two-three seconds of a low-frequency signal indicating wind gusts, with extreme quiet in between, when the instrument was in the eye of the storm.
This drop in pressure also coincided with an increase in temperature near the rover.
From the trajectory taken by the dust devil, the team concluded that the highest density of the dust is at the centre of the vortex and not the high wind areas in the storm’s walls.
When Perseverance was in the eye of the vortex, it recorded wind speeds less than 2 m/s (metres per second), the limit of the sensitivity of the microphone.
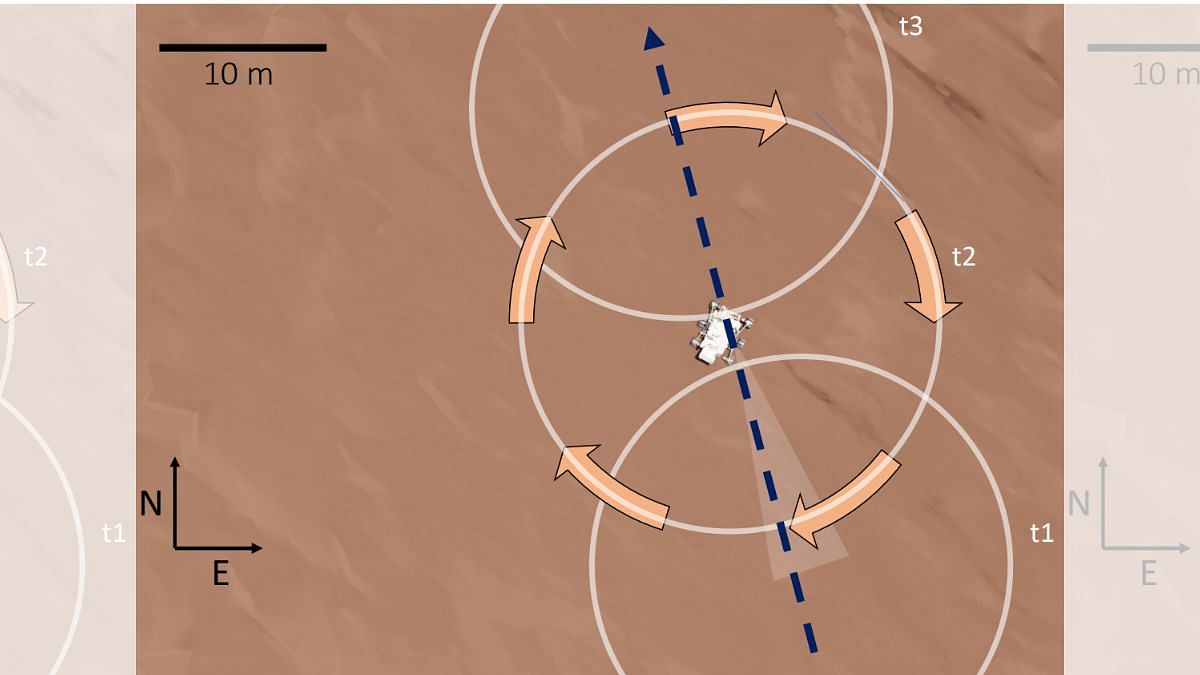
The multi-instrument data and subsequent modelling enabled the team to characterise the dust devil. It was 25m wide, which was almost 10 times larger than the rover it passed over. The vortex was at least 118m tall, about nine-tenths the height of the Great Pyramid at Giza.
The findings show that capturing sound data from other terrestrial planets is useful for studying their atmospheric composition. This is especially true for understanding dust devils on Mars .
As the Perseverance mission continues, more multi-instrument recordings along with microphone data are expected to provide additional information on dust devils and their properties across different sites on the red planet.
(Edited by Poulomi Banerjee)
Also read: NASA launches DART mission to crash into asteroid, results could help defend Earth some day



