New Delhi: Human immunity and its components have never been the topic of such breathless discussion for such a long time. But then, there has never been a time like the Covid-19 pandemic.
Between serological surveys (that check the level of antibodies against the SARS-CoV-2 virus in blood), rapid antigen tests (that test for the part of the virus that kickstarts immune mechanisms) and the quest for vaccines, the immune system is very much ‘in’.
That is also why lymphocytes (a class of white blood cells), especially the ones known as T-cells are the flavour of the season. They are probably the single most important component of the immune system; though given the perfectly synchronised working of the defence mechanism of the body, it may be a little unfair to designate any one as more important than the another.
T-cells play a plethora of roles in immunity — as killer cells that can attack an infected cell and kill it along with the infecting agent, and as suppressor cells that modulate the level of functioning of other lymphocytes. They also have a starring role in the production of antibodies, a function performed by the other variant of lymphocytes called the B cells.
Latest research in Nature shows that presence of T-cells from earlier encounters with coronaviruses could have an important role to play in the body’s immune response, and therefore, a better understanding of it is crucial for the development of a vaccine.
“The published data discussed here indicate that patients with severe COVID-19 can have either insufficient or excessive T cell responses. It is possible, therefore, that disease might occur in different patients at either end of this immune response spectrum, in one case from virus-mediated pathology and in the other case from T cell-driven immunopathology.
“However, it is unclear why some patients respond too little and some patients too much, and whether the strength of the T cell response in the peripheral blood reflects the T cell response intensity in the respiratory tract and other SARS-CoV-2-infected organs,” wrote the researchers from the University of Pennsylvania. They called for more research on the topic.
Turns out, antibodies may or may not last, but T-cells are the new superheroes with the potential to possibly save the planet.
Also read: T Cells – the unsung immune warriors that takeover after coronavirus antibodies wane
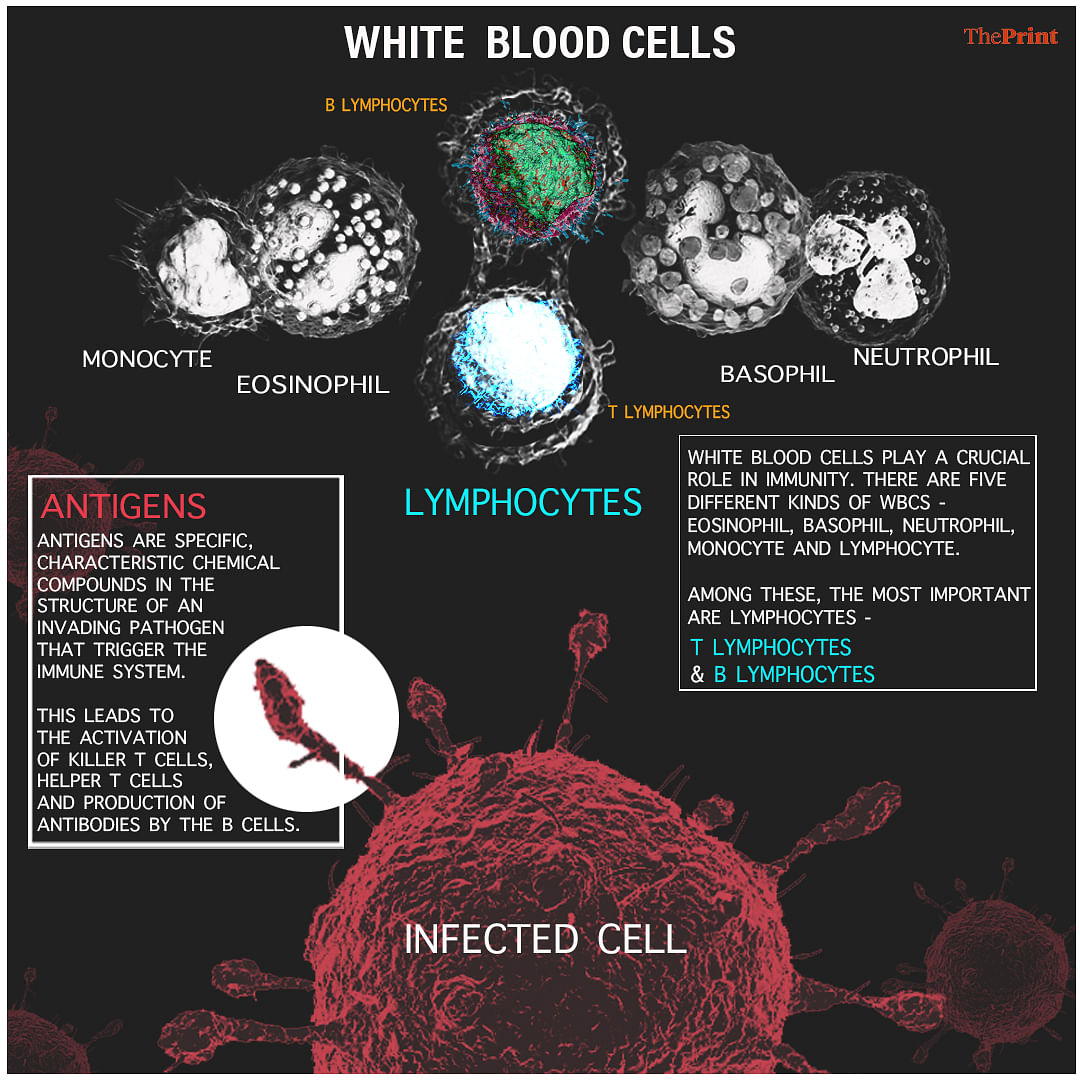
Kinds of immunity
Immunity is of two kinds — innate and acquired.
The defence mechanisms that the body is born with is known an innate immunity. This includes something as simple as the ability of the skin to prevent inner, more vulnerable tissues, from coming in contact with the external environment.
Acquired immunity, as the name suggests, is something that develops over time through exposure to pathogens or disease causing agents like virus and bacteria. Acquired immunity kicks in either through antibodies (this is known as humoral immunity) or through cells programmed to destroy invading organisms by causing the dissolution of the very cells that have been infected.
White blood cells (WBC) play a crucial role in immunity. There are five different kinds of WBCs — eosinophil, basophil, neutrophil, monocyte and lymphocyte. Among these, the most important are lymphocytes, which include the T lymphocytes and the B lymphocytes. However, the others also have important roles to play as supporting cast. For the present discussion, we are concentrating on lymphocytes.
Also read: Immunity boosters are a myth — why you shouldn’t believe claims that promise to fight Covid
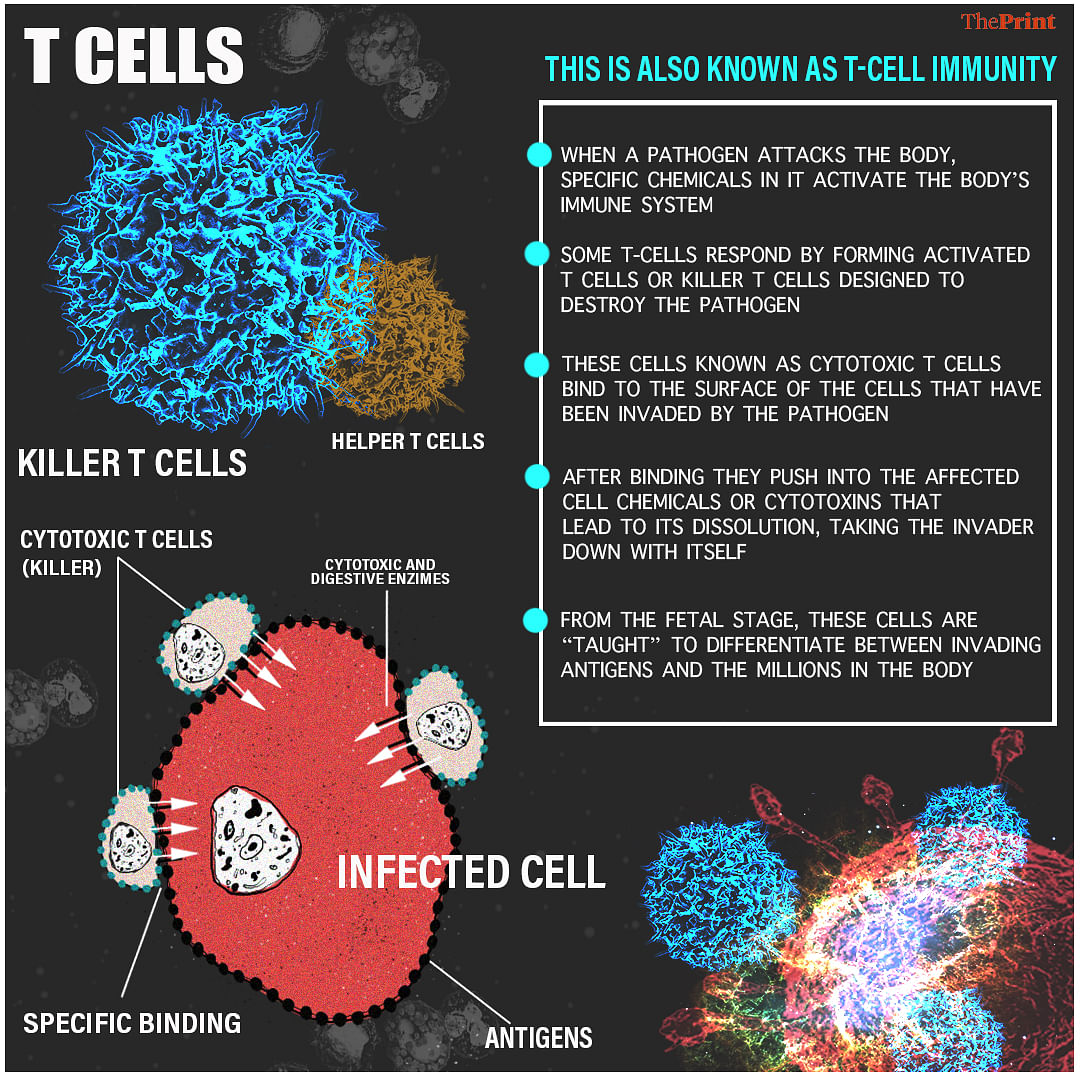
T-cells in cell-mediated immunity
Structurally, under a microscope, very little differentiates a T-lymphocyte from a B lymphocyte. Both varieties are formed in the bone marrow from stem cells, get “trained” in different organs and then lodge themselves in the lymph nodes from where they are deployed when the occasion arises.
The “training” is important. It teaches the cells not to start attacking the body’s own cells. T-cells get trained antenatally (during pregnancy) and for some time after that in the thymus, a small gland present between the lungs only till puberty. B cells are trained in the foetal liver and bone marrow.
When a pathogen invades, specific chemicals unique to it (often proteins or complex carbohydrates) activate the body’s immune system. This activator, which is a unique feature of the invading pathogen, is the antigen. This is what the rapid antigen test looks for.
When an antigen has been detected, the T-cells troop out of the lymph node in an “activated” form and travel to the affected areas to take on the infection. The activated cells, called the Killer T cells, attach themselves to the membrane of the infected cell and with help of cytotoxic chemicals, kill the cell and destroy the invader with it. This is cell-mediated immunity. It is the basis of what happens when transplanted organs are rejected.
The thymus training teaches T-cells to ignore the antigens that are present within the body and not attack them. When that lesson is forgotten, because of genetic or environmental reasons, an autoimmune disorder is triggered.
T-cells in humoral immunity
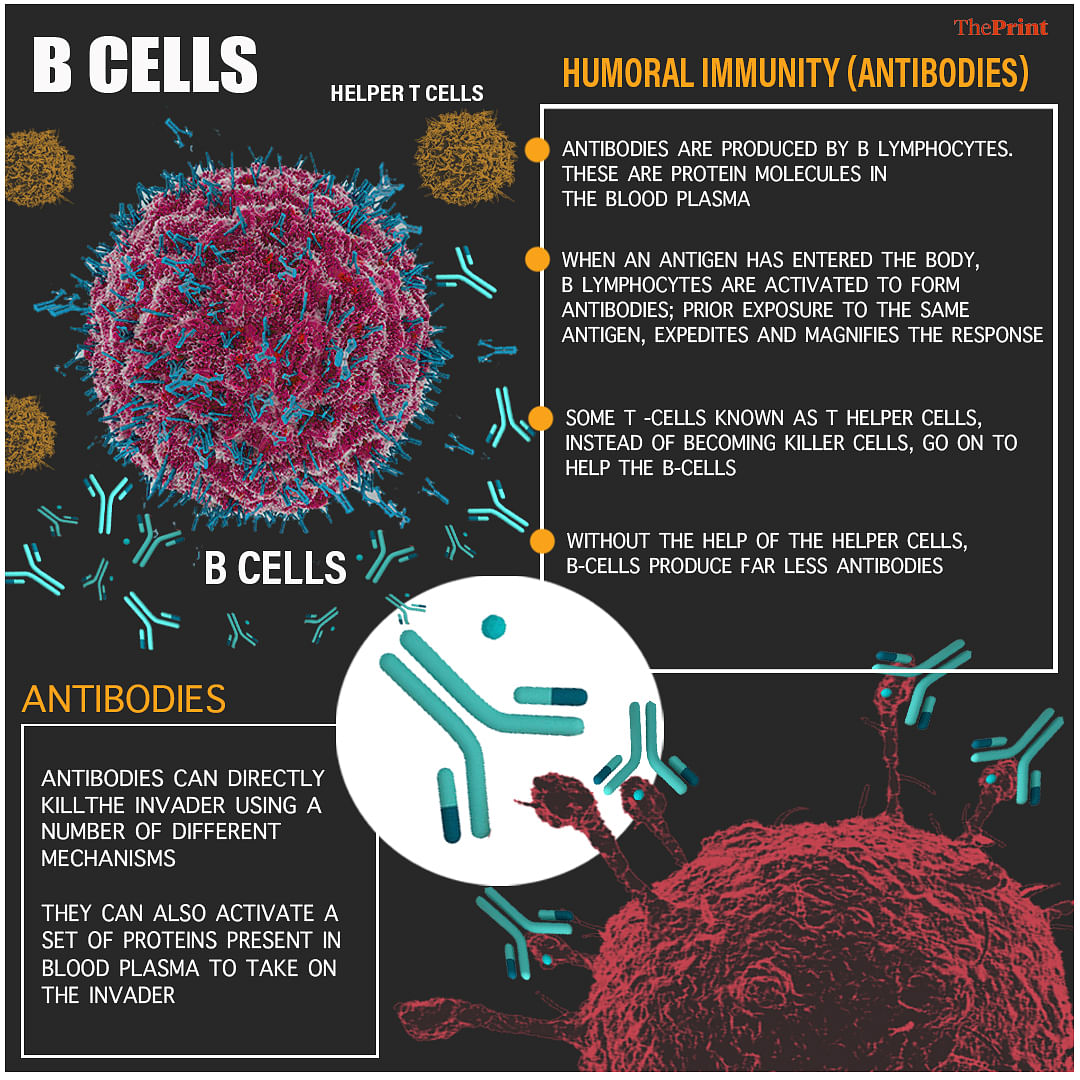
Antigens set in motion a different pathway in the B lymphocytes. These enlarge and start duplicating very rapidly to form many clones, all of which, on maturity, start producing antibodies. The whole process happens very fast.
Antibodies are protein molecules that are present in the plasma, the matrix of the blood in which the cells float. Not all T-cells though turn into cytotoxic killers. Some become what are known as helper T cells, to go and further activate B lymphocytes to produce antibodies. In fact, without these helper cells, the antibody output is not quite sufficient to combat the invading particle.
Antibodies can directly kill the invader using a number of different mechanisms at their disposal. They can also activate a set of proteins present in the blood plasma that in turn can attack the invader using their own pathways.
Once the infection has been tackled, some of the B lymphocytes are tucked away with information about how this was done. These are memory cells that remain dormant until the next invasion happens. These ensure that when an infection recurs, the response is expedited, magnified and is longer lasting. This is the principle behind vaccination — to teach the body to identify and combat a pathogen so that when a future infection happens, the response is stronger.
Also read: An Oxford immunologist breaks down how the university’s vaccine works against Covid-19




Are there any commercial tests for checking the T cell presence in India? If yes any lab which is doing it?
arthritis if not treated properly,creates auto immune disease t cells attack healthy cells,ha roberts homeopath recognised long back treat arthritic toxins first otherwise health cannot be restored.this article is best explaining function of t b cells and antibodies even non doctors can understand.when you recover esp from viral diseases there is problem of loss of taste neuralgic pain here there,homeopathy works better here one should go to govt homeo dispensary.