Some countries are even set to make the leap from developing to developed status, as South Korea has already done.
During the past three decades, there has been a momentous change in the global economy. One of the most troubling and puzzling features — the failure of poor countries to catch up to developed countries — has seemingly been overturned.
Basic growth theory says that developing countries should grow faster than rich ones. One reason is that capital has diminishing returns — as you build more offices, more houses, more cars and machine tools and computers — the economic benefit of building yet more of those things goes down, even as the cost of maintaining them goes up. Second, poor countries can grow fast by copying technology and business practices from rich countries, which is almost always cheaper and easier than inventing new technologies and business practices from scratch.
But, as so often happens in economics, reality has often failed to behave as theory predicts. Economist Lant Pritchett has documented that between 1870 and 1990, inequality between countries soared, with Europe, Japan, the U.S. and a few other countries pulling away from the pack. Of course, much of that divergence was probably due to the impact of colonialism — it’s hard for a country to get rich when it’s under the thumb of another country. But even after decolonization, poor countries struggled to catch up for several decades. Economists Robert Barro and Xavier Sala-i-Martin found that between 1960 and 1985, poor countries continued to lose ground relative to rich ones.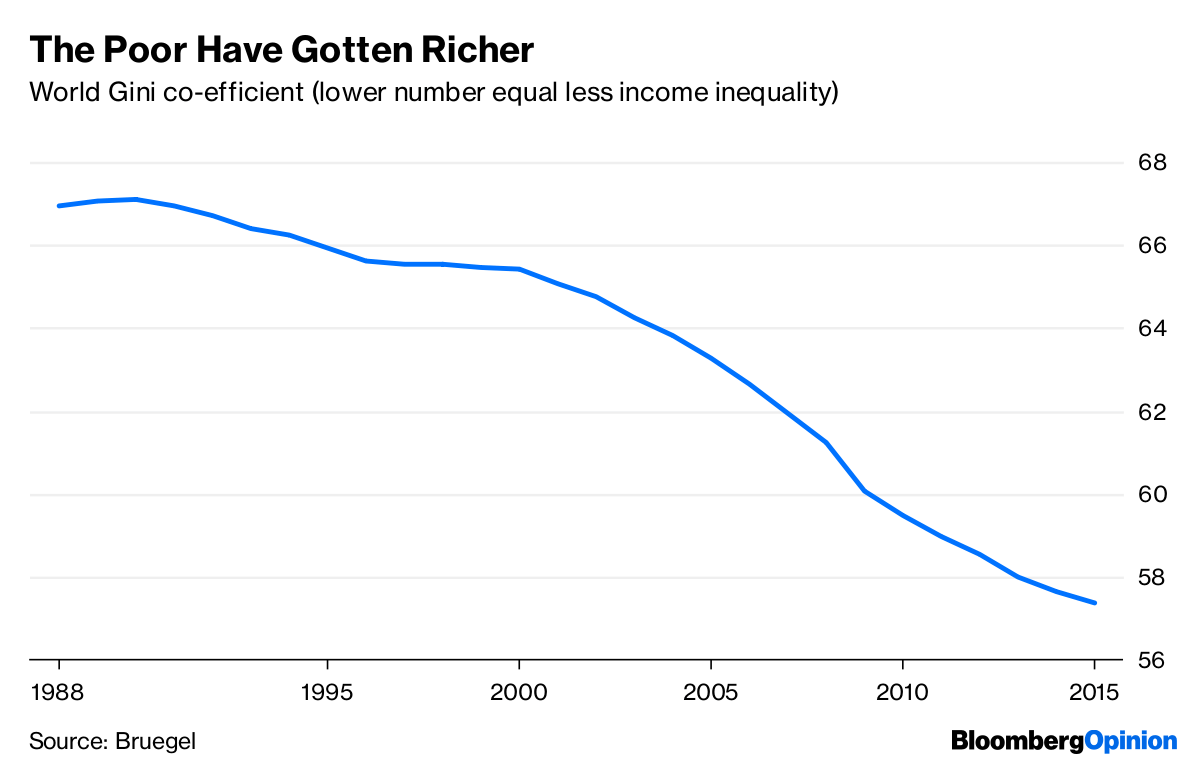
So was growth theory simply wrong? Maybe. All growth theories contain a fudge factor representing a nation’s fundamental capacity for productivity — the education of its populace, the quality of its political institutions, war, damaging government interventions and so on. Controlling for measures of these things, Barro and Sala-i-Martin found that developing nations had tended to catch up — the problem was that too many poor countries fell into civil war or embraced communism or failed to educate their burgeoning populations, degrading the institutions needed to sustain growth. Economists settled on the uncomfortable idea that most poor countries didn’t have what it takes, politically, to grow.
Then something amazing happened. Shortly after Barro and Salai-Martin’s 1992 landmark paper, the story of global growth seemed to change. Many poor countries languished in the 1990s due to low resource prices (poor countries are often natural resource exporters). China, which had been slowly making up lost ground since the end of Mao Zedong’s rule in the 1970s, saw its growth accelerate in the 1990s. India and Indonesia also started to catch up, thanks in part to their own economic reforms.
These countries were so large — together accounting for almost 40 percent of the world’s population — that their growth began to drive down global inequality:
Meanwhile, the divergence documented by Barro and Sala-i-Martin was reversing. Beginning in the 1990s, developing countries started to grow faster than developed ones. Outside of Africa — where a series of bloody wars sent a number of countries into chaos in the 1990s — the pattern was even stronger.
In the 2000s, commodities prices rebounded, and natural-resource exporting countries began to share in the new wave of global growth. Meanwhile, China accelerated yet again, following its entry into the World Trade Organization in 2001 and a burst of productivity growth. The gap between sprinting developing and slow-growth developed countries became even greater.
Then came the Great Recession. Rich countries and poor countries alike were hit hard by the global financial crisis, but — unlike in previous downturns — the poor countries didn’t suffer more. Catch-up continued. Global inequality kept falling.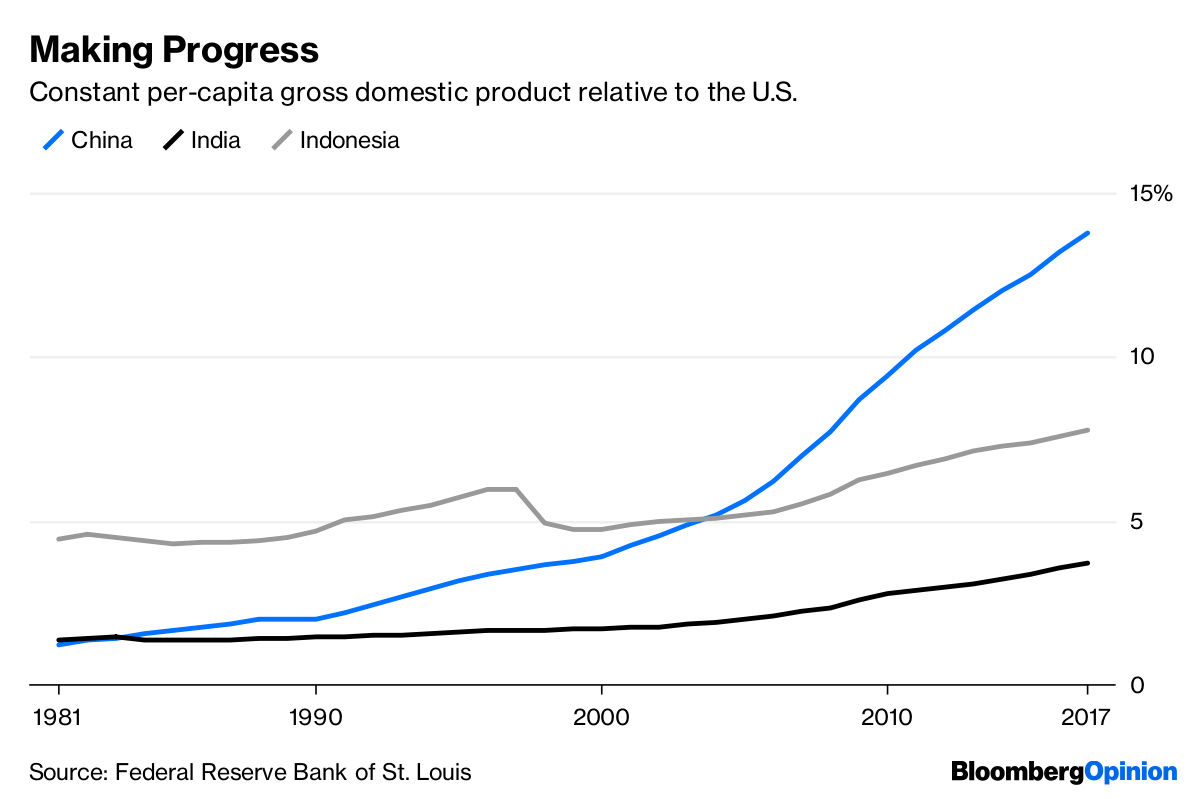 devel
devel
Now, a decade after the crisis, economists are starting to reevaluate their long-held beliefs about global convergence. Dev Patel, Justin Sandefur and Arvind Subramanian of the Center for Global Development recently looked at multiple datasets on per- capita incomes around the world, and found that no matter which measure is used, the relationship between starting income and subsequent growth has been negative since around 1990.
In other words, the idea that rich countries grow more slowly has gone from fiction to fact. No longer do textbook economic theories need to be fudged — reality has caught up. It appears that the war, bad policies, and dysfunctional institutions that afflicted developing nations in the mid- 20th century were a temporary phenomenon.
And the implications for the world are enormous. With economic clout comes geopolitical heft — the influence of the old colonial powers will steadily diminish, while their ex-colonies assume more global leadership. Some countries will even make the leap from developing to developed status, as South Korea has already done. Trade between emerging markets will continue to increase, bypassing the rich economies entirely.
But most of all, the world will simply be a more equal place. Gone are the days when a few countries could lord it over others, secure in the illusion that their society had a secret sauce that others could never emulate. – Bloomberg







I am not an economist. The accepted fact is that as a nation develops it will grow slower than before . The underdeveloped nations in theory should grow the fastest. Therefore it would appear natural the gap should narrow – maybe not in absolute terms because of the base. SOmewhat confused