Warming induced by changes in land use and land cover is contributing to rise in temperature in Eastern India, according to a new study.
Over three decades (1981-2010), the mean temperature in Odisha has recorded an increase of about 0.3 degree Celsius. The highest temperature rise of 0.9 degrees Celsius has been recorded during the years 2001 to 2010.
Change in land use and land cover is responsible for half of this rise in temperature, according to the study done by researchers from Indian Institutes of Technology at Bhubaneswar and Kharagpur, along with those from Southampton University. Researchers analyzed satellite data on land use, land cover as well as temperature in various parts of the state.
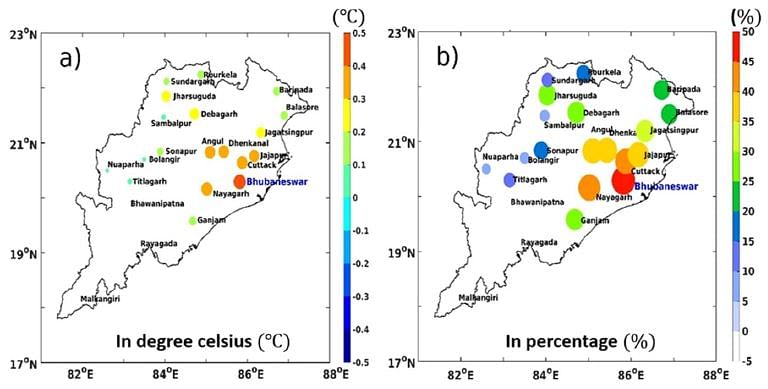
The temperature in big cities is greater than in smaller cities. The mean temperature rise in Cuttack and Bhubaneswar, which have seen high urbanization in the past three decades, has been 40 and 50 percent respectively in three decades. Other cities where temperature increase has been recorded are Angul, Dhenkanal and Jajapur.
“We have found that regions having largest land use and land cover induced warming coincided with those regions where cropping patterns are altered. Mostly a shift from kharif to rabi has led to warming of up to 30 percent,” explained Dr V. Vinoj, researcher at IIT Bhubaneswar, while speaking to India Science Wire.
Rabi crop cultivation has increased by 97 percent in Odisha between 2004 and 2010. There has been a decrease in Kharif crops, reflecting agricultural diversification and changing cropping patterns. Changes in soil moisture content affects land surface temperature.
Also read: India can’t commit to climate change abroad and be non-compliant on environment at home
“Between 25 to 50 percent of warming is due to change in land use as a consequence of both changing cropping patterns and urbanization. In addition, urban areas show warming that is double that of the rural areas”, added Dr. Vinoj.
The rise in temperature in any location is a combination of effects that are local in origin such as deforestation and urbanization and those that are forced externally as part of global or regional changes. Emission reduction must be the main goal, but planned and sustainable agricultural and forestry management too are very critical, according to the researchers.
The study team included Partha Pratim Gogoi, Dr. V. Vinoj, D. Swain, G. Roberts, J. Dash, and S. Tripathy. The research results have been published in journal Scientific Reports.
This article was originally published in India Science Wire.
Also read: Most of us were born into climate change — it’s the only world we’ve ever known



