There is now a 95% chance COVID-19 has been eliminated in New Zealand, according to our modelling, based on official Ministry of Health data.
As of June 4, New Zealand has had 20 consecutive days of zero new cases, with only one active case remaining. The last new reported case of COVID-19 was on May 15 (going by the date the case was first suspected rather than later confirmed).
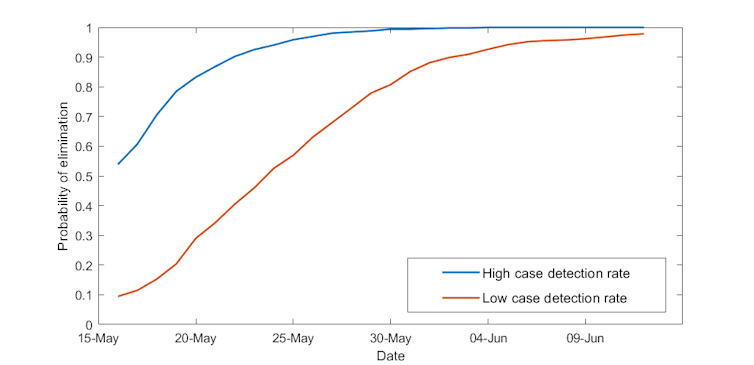
This still leaves a small chance of undetected cases, and we know that COVID-19 is passed on at superspreading events.
New Zealand is now preparing to relax its COVID-19 restrictions to alert level 1 from as early as next Wednesday, which would end physical distancing and size restrictions on gatherings. But our modelling suggests removing limits on large gatherings will increase the risk of a very large new outbreak from 3% to 8%.
To reduce this risk, New Zealanders will need to continue avoiding the three Cs of possible infection: closed spaces, crowded places and close contact.
As crowds return, the risks will rise
New Zealand is now very close to its elimination target. But there is still a 5% chance of undetected cases.
On June 3, Prime Minister Jacinda Ardern announced details of the impending alert level 1 rules. Border closures will largely remain (except for returning New Zealanders) but all other significant restrictions on people’s movement within New Zealand will end.
From the perspective of the virus, the most significant change will be the end of restrictions on the size of gatherings. Airlines can fill up economy class again, nightclubs can pack their dancefloors and universities can open their lecture theatres.
Someone who caught the virus three or four weeks ago may not have developed severe symptoms (which happens in around 30% of people) and not got a test. They could have passed the virus on to someone else, who also missed out on a test.
A chain of infections like this could continue for a while before it is detected. Some segments of the population, such as younger people, are less likely to develop symptoms and are therefore more likely to sustain hidden infection chains.
Also read: How Sweden’s ‘model’ Covid strategy collapsed due to arrogance in scientific approach
COVID-19 is a superspreading virus. The reproduction number (R0) tells us that on average each infected person infects another 2.5 people. But for every ten people who catch COVID-19, nine probably won’t pass it on, while the tenth person may turn up at an event and infect 25 others.
Risk from returning travellers
There is also a chance COVID-19 could enter New Zealand with an international traveller. Last week, around 200 people, almost all returning Kiwis, touched down in New Zealand every day.
Many came from places like Australia, Hong Kong or Tonga – all countries relatively free of COVID-19. Some also arrived from the USA, where the virus is widespread. Between February and April, we know that between 0.1% and 0.2% of all arrivals tested positive. With these numbers, we should expect one or two new cases to arrive each week.
New arrivals must remain in quarantine for at least 14 days. The incubation period for COVID-19 is usually five to six days and it is rare for symptoms to begin more than 14 days after being exposed.
The bigger risk is a symptom-free person arriving and passing the virus onto someone at the same quarantine hotel, who then leaves before their symptoms appear.
Ministry of Health data show eight of New Zealand’s 500 imported cases developed their first symptoms more than two weeks after arriving. Maybe they caught it before they arrived or maybe they caught it during quarantine. Either way, they would have been infectious after they left quarantine.
People who work at the border – airline cabin crew, biosecurity or immigration personnel and staff at quarantine hotels – are at similar risk.
The inevitable new case
Our models show the risk of new cases coming from within New Zealand is now comparable to that from international travellers. The risk from international arrivals stays about the same whether we’re at level 1 or 2, while the risk of domestic transmission is decreasing.
The most important question is how we will cope when the inevitable new case arrives.
Each active case is like a small spark waiting to start a fire. Superspreading theory tells us most of those sparks go out, but a small number will ignite. These sparks are the problem: it could be an infected person at a choir rehearsal, at a nightclub, or cheering for their sports team.
New Zealand is fortunate to have highly trained, experienced contact tracers standing by. But they need our help. If you were to test positive, could you remember everywhere you have been for the last week and who else was there? A contact tracer’s nightmare is a large gathering with no record of who attended.
To move to level 1, we first need to ensure our contact tracing systems, including the NZ COVID Tracer app, QR codes and sign-in sheets at shops, are up to scratch. We need to be confident we can manage the risks when hundreds of people gather or attend protest marches. We have to be able to do these things safely while COVID-19 is still out there.
![]()
Michael Plank, Professor in Mathematics, University of Canterbury; Alex James, Associate professor, University of Canterbury; Audrey Lustig, Research scientist, Manaaki Whenua – Landcare Research; Nicholas Steyn, Research assistant; Rachelle Binny, Research scientist, Manaaki Whenua – Landcare Research, and Shaun Hendy, Professor of Physics
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Also read: The real reason why countries with women leaders are handling Covid crisis better






