India has chosen an odd combination of strategies in its fight against the coronavirus: a harsh lockdown on economic activity and a meager fiscal response to the loss of jobs and incomes.
What’s making this more painful is a denial of the role of finance in both containing the fallout of the outbreak and in supporting the recovery later.
Allowing a credit contagion to take hold is a serious error, especially as India’s under-capitalized lenders were swamped by corporate defaults even before Covid-19 struck. As both retail and institutional loans go sour at a rapid pace, the financial sector will amplify the shock of virus-related shutdowns and hobble the return to anything resembling normalcy.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi has extended an expiring 21-day national shutdown to May 3, promising to relax some curbs after Monday in areas that aren’t likely to become disease hotspots.
Leave aside the problem of determining safe zones when the government isn’t testing enough for infections, which have crossed the 10,000 mark. Beyond a token $22.6 billion plan announced March 26, the Modi administration has shied from concrete steps to help the working class survive their loss of livelihood. The lapse is made worse by a monetary authority seemingly oblivious to the crumbling of a shadow-banking industry that’s been struggling with high funding costs for nearly two years now. Lowering the benchmark interest rate or boosting liquidity by $50 billion is of little use when those who need the money are simply not getting it.
This approach needs to change. Let Team Modi figure out a fiscal strategy, and then let the Reserve Bank of India step in to support it. This will mean copying the U.S. playbook, where programs like Paycheck Protection, targeted at small firms and their employees, and Main Street Lending, aimed at bigger firms, are government backed with the Fed providing funding to banks making the loans.
The template will need to be tweaked to fit the Indian economy’s highly informal setup, marked by a near-complete absence of social safety nets — barring a rural job guarantee that pays less than the minimum wage in agriculture. A quarter of the workforce consists of migrants who go back and forth between urban centers and their village homes. They suddenly have no work and no money to buy food or pay rent. Even with the government’s promise of distributing free food, the 500 rupees ($6.5) a month it has started crediting into no-frills bank accounts held by women is paltry.
Also read: How India can buck the trend of global recession caused by coronavirus
India’s 29 states, which are closer to the unfolding humanitarian disaster, are balking at high costs the market is charging them for long-term money. For now, they might make do by tapping their recently enhanced temporary overdraft with the central bank. However, as their expected $100 billion share of federal taxes takes a big hit, they, too, would have no option except to hawk their bonds in a tight market. If the Fed can cross a political line by doing something it’s never done before — offering to lend $500 billion to U.S. municipalities and states — there’s no reason for the RBI to play coy.
Now that the lockdown has been extended, it’s prudent to pencil in a further two-week delay before the restrictions are relaxed meaningfully. In such a scenario, where supply chains resume only gradually, the number of people who might lose their ability to subsist would quadruple, and the nonperforming loan ratio could swell by 7 percentage points, according to McKinsey & Co. The cost of helping households, companies and lenders, could exceed $130 billion, or more than 5% of gross domestic product.
Knowing this, why isn’t India committing 1% of GDP now? Say, the Finance Ministry puts down $25 billion equity into a special purpose vehicle. (That’s a third of the support the U.S. Treasury is similarly providing the Main Street Lending Program.) Let this financing vehicle purchase 95% of lenders’ interest in loans they make to vulnerable firms, shadow banks, individuals and even states, with the RBI lending seven rupees to it for every rupee contributed by the ministry. This eightfold amplification of the original firepower will make $200 billion of loans available. The first loss will be absorbed by the government, as it should be.
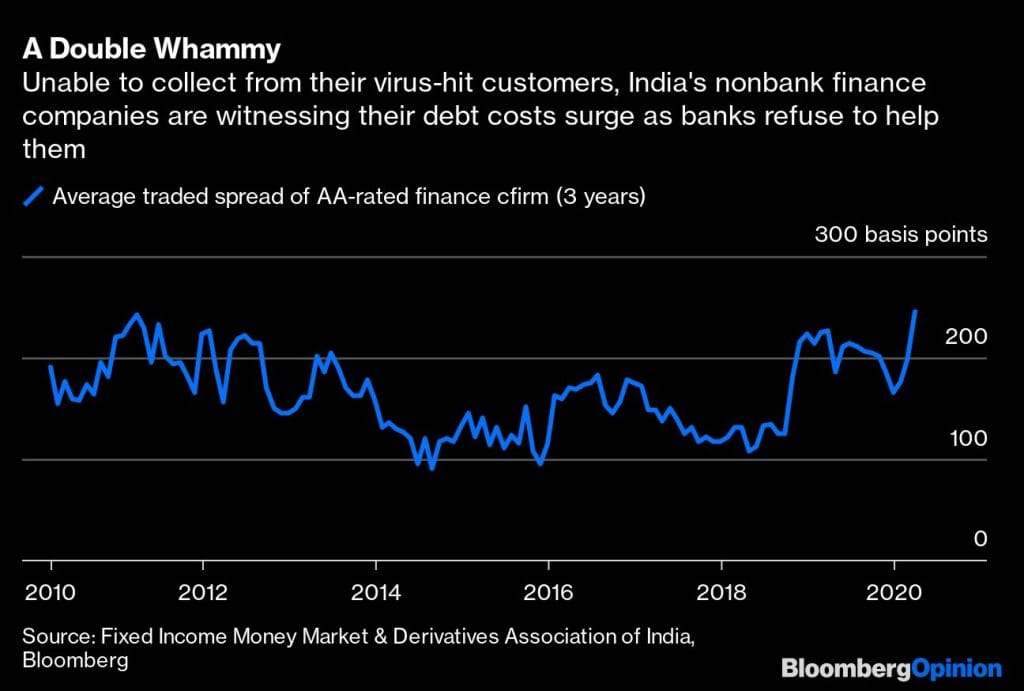
The RBI’s present strategy is not working. The three-month freeze it has recommended on loan repayments has boomeranged on shadow lenders, who have become increasingly important in recent years for meeting the credit needs of individuals and small firms. The financiers aren’t getting a moratorium on what they owe banks, while being forced to offer it to retail customers, many of whom can’t pay now, anyway.
Debt mutual funds, which also lend to these nonbank financiers, are exercising put options on their bonds, making it even harder for the industry to survive this crisis. The collapse and botched rescue of Yes Bank Ltd. has bred anxiety among depositors about leaving their money in second-tier, private-sector banks. The cheap funds the RBI has promised lenders if they invest in corporate bonds are getting parked in the debt of higher-rated firms.
When the moratorium is over, many of the loans held in abeyance will turn bad. The interest that lenders are booking (but not receiving) will need to be written off. India will have to resort to a sweeping nationalization of its finance industry to restart the economy. That will cost multiples of $25 billion. Why not lower that future obligation by giving a chance at survival to those who were solvent before the coronavirus and can be made whole once again? –Bloomberg
Also read: Great Lockdown Depression will be the worst in a century and could get worse, IMF warns






