Modi wants banks to dole out loans quickly to keep world’s fastest growing major economy firing. RBI governor Urjit Patel has other priorities.
Mumbai: India is the latest country to see age-old tensions between governments and central banks flare up as the era of easy money draws to a close.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s government sent the central bank letters that cited a never-used power to overrule the Reserve Bank of India in a bid to push through measures that would unleash spending ahead of an election, Bloomberg reported Wednesday. That triggered a feisty speech from a central bank deputy in defense of independence, which brought the spat into the open.
As the rift looked set to deepen Wednesday, the government appeared to ease tensions, issuing a statement saying it “respects and nurtures” central bank autonomy. That helped the rupee claw back some of its losses while the benchmark stock index surged 1.6 percent on speculation the situation may improve now.
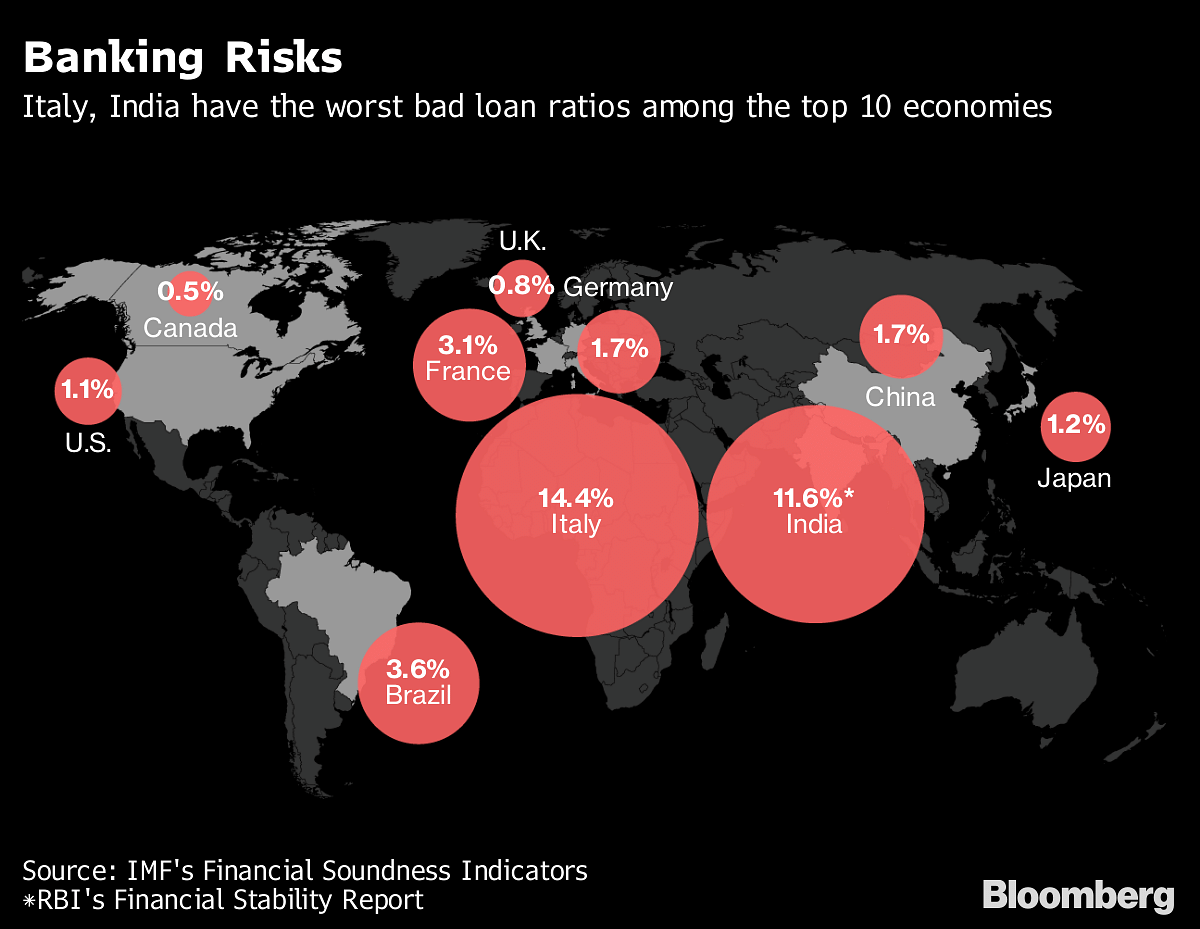
The tension in India mirrors central bank fights playing out in countries as varied as the U.S. and Turkey, and is unlikely to go away soon. Modi faces reelection next year, and he wants banks to dole out loans quickly to keep the world’s fastest growing major economy firing. Wary of already high bad debts, emerging market strains that are pressuring the rupee and threatening to add to inflation, central bank Governor Urjit Patel has other priorities.
Why Central Banks Have Become Political Punching Bags: QuickTake
“The Indian government is treading on dangerous ground with a number of moves that could put the independence of the RBI at risk,” said Shilan Shah, senior India economist at Capital Economics in Singapore. “A loss of credibility for the central bank could jeopardize its efforts to rein in inflation, which has been one of the big policy successes in India over the past few years.”
The battle comes at a bad time for India. The economy is facing risks from elevated oil prices, a weak currency and a crisis in the shadow banking sector.
While Modi’s coalition is facing the possibility of a reduced majority in the next election, there’s a slim chance disparate opposition parties could unite to oust him. The central bank conflict lends itself to the view held by Modi’s critics that he has mismanaged the economy and is stomping over independent agencies.
“For the health of India’s economy and institutions, the contingencies of politics must not be allowed to overrule the demands of fiscal and monetary prudence,” said Nikita Sud, Associate Professor at the University of Oxford.
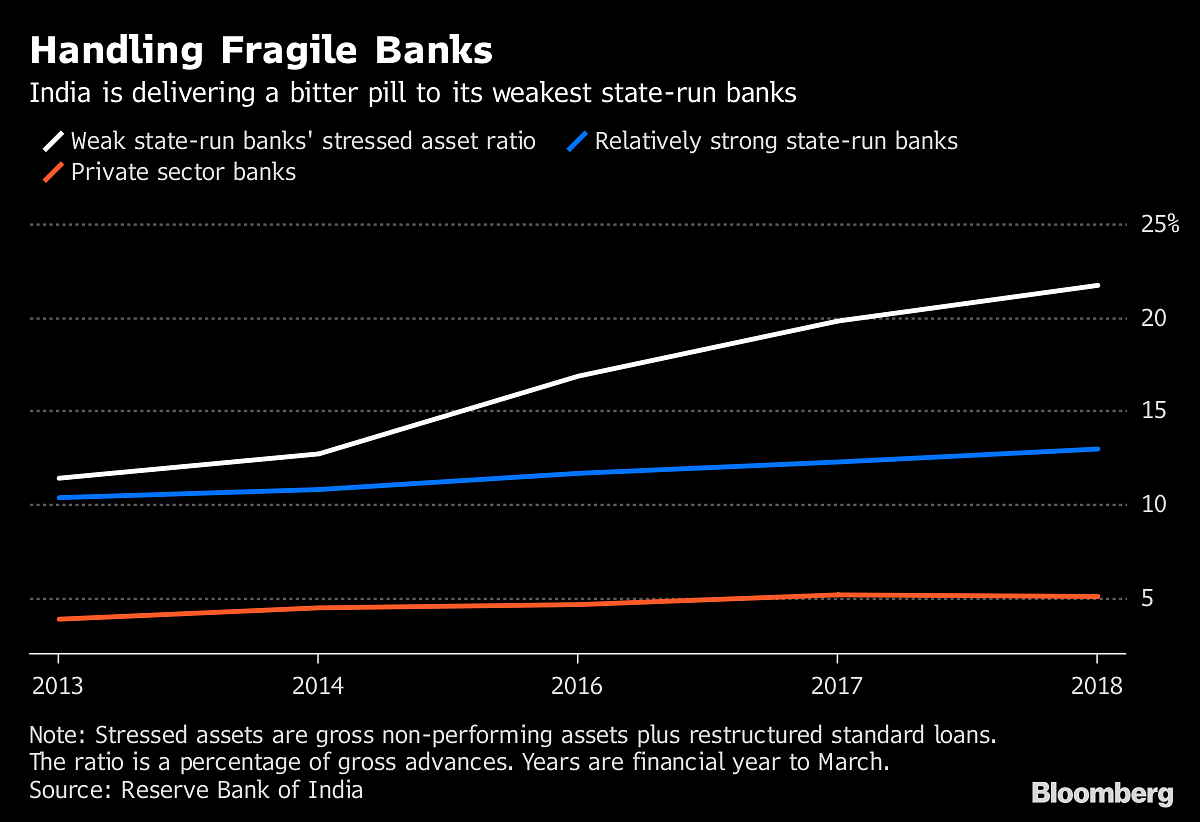
Earlier this month, Modi kicked up a political storm when his government removed the chief of the Central Bureau of Investigation, India’s equivalent of the U.S. Federal Bureau of Investigation. The Supreme Court is now scrutinizing the decision, which opposition leaders said was done to block a probe into a controversial $8.7 billion fighter jet deal.
Tensions Anew
India’s central bank versus government tensions aren’t unique. Patel’s predecessor, Raghuram Rajan decided to head back to the University of Chicago after only one term. Rajan had faced criticism from a prominent Modi ally who accused the former IMF chief economist of keeping interest rates too high. Many bankers also complained about Rajan’s aggressive efforts to clean up bad debt at state-owned lenders.
In 2013, Rajan’s predecessor Duvvuri Subbarao also fell out with then-finance minister Palaniappan Chidambaram, who complained high interest rates were an impediment to economic growth.
Patel took helm at the central bank in 2016. The governor was initially seen as being more supportive of Modi’s policies compared with the outspoken Rajan. He was also instrumental in setting up a Monetary Policy Committee that tied policy making to an inflation target of 4 percent in the medium term.
As part of that mandate, the RBI resorted to back-to-back rate hikes this year and tightened liquidity. The tighter conditions are likely to hurt growth, and with banks busy prioritizing bad loans resolution over new lending, the government faces a tough task of ensuring consumption — the bedrock of the economy — doesn’t fall off the cliff.
What Our Economists Say… The rift between the government and the Reserve Bank of India is largely about a liquidity deficit in the economy, which is restricting non-banking finance companies access to funds.– Abhishek Gupta, Bloomberg Economics
The RBI’s top brass, though, is determined not to sweep the bad loans problems under the rug even if it comes at the cost of growth before an election year. Last week, Viral Acharya said the central bank wanted more powers to discipline errant government-owned banks, echoing Patel’s comments earlier this year.
“The government should be mindful that as long as the disagreements stay as divergent opinions meant only for public posturing, a market backlash can be avoided,” said Rudra Sensarma, a professor of economics at the Indian Institute of Management in Kozhikode. The RBI also needs to convince the government “that its persistence with high interest rates and clampdown on errant banks are in the best interest of economic growth.” – Bloomberg



